

So, we can choose our public key, E as 5 since it isn’t a factor of 2 or 3. Now, we have to select a public key, say p, so that isn’t a factor of (A-1) and (B-1). įor this example, let’s try and work the RSA Encryption Algorithm with random prime numbers, say 7 and 17. Want to become an expert in cyber security and build a successful career, go through Intellipaat’s Cyber Security course. You can decrypt the plaintext from the ciphertext using this equation:.Once the ciphertext is generated, it should be sent to the recipient.You can calculate the ciphertext from the plaintext using this equation:.The private key should match this equation: Now you can select the private key for decryption say, D.You have to make sure this key isn’t a factor of (A-1) and (B-1).

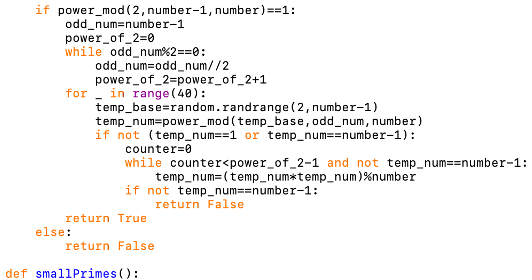
You have to select a public key, say E, for encryption.Next, you can find the product of A and B, say N.You can choose any two large prime numbers, say A and B.This means that only the person who created the public key will be able to generate the private key as well. The decryption would require knowledge of the two prime factors of that number and there is no known method to find the prime factors of such numbers. The public key would be the product of two large prime numbers. In the RSA Encryption Algorithm, a public key is used for encryption and a private key, different from the public key and only known to the recipient, is used for decryption.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
